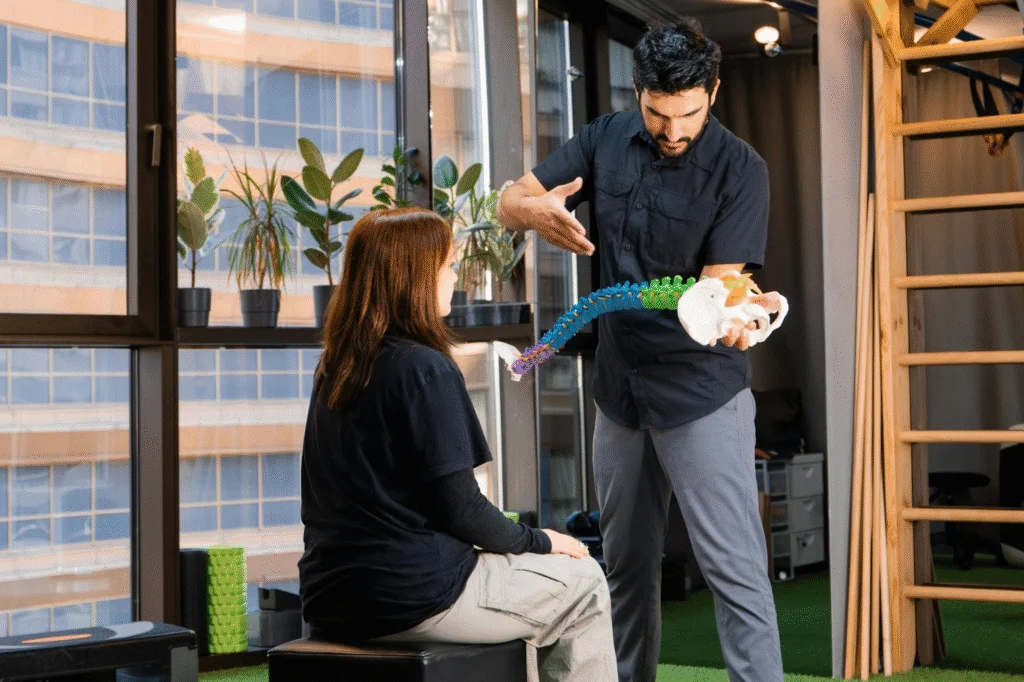
Back pain is a prevalent condition affecting individuals of various ages and lifestyles. In New Jersey, understanding the critical junctures for consulting a back pain specialist is pivotal. Persistent pain, severe discomfort, or symptoms like numbness and difficulty with daily functions may indicate underlying issues such as degenerative disc disease or nerve compression. Timely evaluation by a specialist is indispensable to prevent long-term complications. But what specific signs necessitate expert intervention?
Persistent Pain Lasting More Than a Few Weeks
When back pain persists for more than a few weeks, it transcends the category of acute discomfort and may indicate underlying pathophysiological conditions requiring expert evaluation. This chronic manifestation often correlates with progressive worsening pain levels and mobility limitations, which can remarkably impair daily functioning. Identifying the etiology is pivotal, as persistent pain may derive from degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis, or other structural abnormalities. Clinical assessment should encompass both subjective reports of pain intensity and objective evaluations of functional capacity. Evidence-based diagnostic tools, such as MRI or CT imaging, can elucidate the anatomical sources of pain, guiding targeted therapeutic interventions. Early specialist involvement is indispensable to mitigate the risk of long-term disability and enhance patient quality of life through tailored treatment strategies.
Experiencing Severe or Debilitating Pain
Persistent back pain can sometimes escalate into severe or debilitating pain, profoundly impacting an individual’s ability to perform routine activities and diminishing quality of life. Such pain may cause significant functional limitations, including the inability to sleep and difficulty with exercise. Seeking advanced care from back pain experts in NJ is advisable to understand the underlying causes and to formulate an evidence-based management plan. Key indicators for consulting a specialist include:
- Persistent pain despite conservative management: Not alleviated by rest, physical therapy, or medication.
- Inability to sleep: Pain intensifies at night, disrupting rest and recovery.
- Difficulty with exercise: Reduced capacity to engage in physical activity, leading to deconditioning.
- Increased reliance on analgesics: Frequent use of pain medication to manage symptoms.
- Interference with occupational duties: Pain impairs ability to work effectively.
Pain Accompanied by Numbness or Tingling
Although back pain is a common complaint, the presence of accompanying numbness or tingling may suggest a more complex underlying condition requiring specialized evaluation. Such symptoms often indicate the involvement of pinched nerves, where nerve roots become compressed or irritated. This compression can lead to radiating discomfort, potentially extending from the spine to the extremities, and is frequently associated with conditions such as herniated discs or spinal stenosis. The manifestation of numbness or tingling, particularly when chronic or worsening, warrants a thorough assessment by a back pain specialist. Diagnostic imaging, such as MRI or CT scans, may be employed to identify the precise etiology. Prompt intervention can prevent further neurological impairment and optimize therapeutic outcomes, emphasizing the need for timely consultation.
Difficulty With Daily Activities
Many individuals with back pain experience significant difficulty performing daily activities, which can severely impact their quality of life. This condition often results in the inability to complete essential tasks due to compromised mobility. Evidence suggests that persistent back pain can lead to the avoidance of routine activities, further exacerbating functional limitations. The following issues may arise:
- Impaired ability to lift or carry objects, affecting household chores.
- Difficulty with prolonged standing or walking, hindering occupational performance.
- Challenges in bending or twisting motions, restricting personal care routines.
- Reduced capacity for sitting for extended periods, impacting sedentary work.
- Altered gait or stance, leading to further musculoskeletal strain.
Such limitations necessitate an extensive evaluation by a back pain specialist to devise targeted interventions.
Pain Following an Injury or Accident
Injury-induced back pain can arise from a variety of traumatic events such as falls, automobile accidents, or sports injuries, where the mechanical integrity of the spinal structures is compromised. The initial manifestation of new injury symptoms may include localized pain, swelling, and restricted range of motion. Clinicians should be vigilant for worsening pain patterns, which could indicate more severe underlying issues such as vertebral fractures, herniated discs, or ligamentous damage. Persistent discomfort or escalation of symptoms warrants further diagnostic evaluation through imaging modalities like MRI or CT scans. It is indispensable for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek a consultation with a back pain specialist in New Jersey, as timely intervention can prevent chronic dysfunction and facilitate ideal recovery outcomes.
Noticeable Changes in Bowel or Bladder Function
Noticeable changes in bowel or bladder function can be indicative of urgent medical symptoms that necessitate immediate evaluation by a healthcare professional. Such changes may serve as neurological warning signs of conditions like cauda equina syndrome, where prompt intervention is indispensable to prevent permanent damage. Evidence-based guidelines recommend that any sudden onset of urinary retention, fecal incontinence, or saddle anesthesia in conjunction with back pain should be addressed urgently by a specialist.
Urgent Medical Symptoms
Significant alterations in bowel or bladder function may signal urgent medical conditions requiring immediate attention. Such changes, when accompanied by sudden onset back pain or back pain with fever, could indicate serious underlying pathologies. Healthcare professionals assess these symptoms to determine the potential for conditions such as cauda equina syndrome or spinal infections, which necessitate prompt intervention.
Key indicators include:
- Inability to urinate or control urination
- Incontinence of the bowel or bladder
- Severe, sudden onset back pain, especially with fever
- Numbness or tingling in the groin or buttocks
- Persistent and escalating pain radiating to the legs
When these manifestations are present, consulting a back pain specialist in New Jersey guarantees timely diagnosis and management, potentially preventing irreversible complications.
Neurological Warning Signs
Although often overlooked, alterations in bowel or bladder function can serve as critical neurological warning signs indicative of serious spinal conditions. Such changes may hint at underlying nerve damage, potentially resulting from conditions like cauda equina syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by compression of the cauda equina bundle at the lower end of the spinal cord, leading to urinary retention or incontinence, bowel dysfunction, and saddle anesthesia. These symptoms arise due to impaired nerve signaling, which may also trigger muscle spasms in the lower back and legs. Prompt evaluation by a back pain specialist is warranted to prevent irreversible damage and to implement timely interventions. Diagnostic imaging and neurophysiological assessments are essential to ascertain the extent of nerve involvement and to guide appropriate management.
Pain That Radiates Down the Legs
When experiencing pain that radiates down the legs, often referred to as sciatica, it is pivotal to understand the underlying pathophysiology to effectively diagnose and treat the condition. Sciatica typically results from lumbar nerve root compression, necessitating an extensive radicular symptoms evaluation. Effective sciatica management involves identifying factors such as disc herniation or spinal stenosis.
- Pathophysiology: Compression of the sciatic nerve can lead to debilitating symptoms.
- Diagnostic Imaging: MRI or CT scans are instrumental in visualizing nerve impingement.
- Clinical Evaluation: Detailed patient history and neurological examination are critical.
- Conservative Treatments: Physical therapy and anti-inflammatory medications are first-line interventions.
- Referral Indications: Persistent symptoms or neurological deficits warrant specialist consultation.
Early intervention can prevent progression to chronic pain syndromes, optimizing patient outcomes.
Unsuccessful Relief From Over-The-Counter Treatments
Many patients with back pain initially turn to over-the-counter (OTC) treatments, expecting symptomatic relief. However, an inability to find relief from these interventions often prompts further concern. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and analgesics are commonly utilized OTC options, targeting inflammation and pain reduction. Despite adherence to recommended dosages, some individuals experience worsening symptoms despite treatment, indicating a potential underlying pathology unresponsive to OTC interventions. This scenario necessitates a thorough evaluation by a back pain specialist. Persistent back pain unmitigated by OTC treatments may suggest conditions such as disc herniation, spinal stenosis, or other structural abnormalities. Early consultation with a specialist can facilitate accurate diagnosis and formulation of a targeted treatment plan, mitigating further deterioration and enhancing patient outcomes.
Chronic Back Pain Despite Lifestyle Modifications
Despite implementing evidence-based lifestyle modifications, individuals with chronic back pain often experience persistent pain symptoms that greatly/tremendously/enormously/substantially impact their quality of life. Research indicates that common home remedies such as ergonomic adjustments and physical activity may be insufficient for some patients, leading to the necessity for specialized intervention. This underscores the importance of consulting with a back pain specialist to explore advanced therapeutic options tailored to individual patient needs.
Persistent Pain Symptoms
Even after implementing thorough lifestyle modifications, a subset of individuals continues to experience chronic back pain, indicating a complex interplay of underlying factors. Persistent pain may result from muscle weakness and reduced mobility, both of which can exacerbate the condition. These symptoms often necessitate medical evaluation to identify potential structural or neurological causes. Key considerations include:
- Muscle Weakness: Contributes to inadequate spinal support, intensifying pain.
- Reduced Mobility: Limits physical function, hindering daily activities.
- Neurological Impairments: Potential nerve involvement may require advanced diagnostics.
- Structural Abnormalities: Disc degeneration or vertebral misalignments could be contributory.
- Chronic Inflammation: Persistent inflammatory responses may aggravate pain symptoms.
Addressing these elements through a specialist’s guidance can offer a targeted treatment strategy, promoting effective pain management and enhanced quality of life.
Ineffective Home Remedies
While numerous individuals resort to home remedies to manage chronic back pain, evidence suggests that these methods often fail to provide substantial relief when lifestyle modifications alone prove insufficient. Natural remedies, such as herbal supplements and topical applications, lack robust clinical evidence supporting their efficacy in chronic back pain management. Additionally, reliance on natural remedies without professional guidance can lead to medication misuse, exacerbating underlying conditions or introducing adverse effects. Chronic back pain necessitates an extensive treatment approach that may include medical interventions beyond self-management strategies. Persistent symptoms, despite attempts at lifestyle alterations, indicate the need for professional evaluation. A back pain specialist can offer advanced diagnostic tools and tailored interventions, ensuring an evidence-based approach to pain management and optimizing patient outcomes.
Back Pain With Unexplained Weight Loss
Occasionally, patients present with a concerning combination of back pain and unexplained weight loss, which can signal underlying systemic conditions requiring prompt evaluation. Such clinical manifestations may indicate malignancies, infections, or metabolic disorders. Associated symptoms like unexplained muscle weakness and sudden mobility restrictions warrant immediate medical attention. A thorough diagnostic approach is essential to identify the etiology, including imaging studies and laboratory tests.
Potential conditions include:
- Spinal tumors: May lead to both weight loss and neurological deficits.
- Infectious processes: Osteomyelitis or spinal tuberculosis.
- Endocrine disorders: Hyperthyroidism causing catabolic states.
- Metastatic disease: Cancer spread to spinal structures.
- Inflammatory diseases: Systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis.
Patients exhibiting these signs should consult a specialist to guarantee timely intervention and appropriate therapeutic strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Qualifications of a Back Pain Specialist?
A back pain specialist’s qualifications include extensive training and expertise in musculoskeletal disorders. Specialty certification requirements often encompass board certification in fields like orthopedics, neurology, or physical medicine and rehabilitation, ensuring evidence-based care for patients.
How Can I Find a Reputable Specialist in New Jersey?
To identify top rated specialists in New Jersey, individuals can consult databases such as Healthgrades or the American Board of Medical Specialties. Guaranteeing local insurance coverage secures cost-effective access to reputable practitioners with proven expertise.
Are There Specific Tests a Specialist Might Perform?
A specialist may conduct diagnostic imaging tests like MRIs or X-rays, complemented by physical examination techniques, to assess back pain. These methods provide evidence-based insights into potential underlying conditions, guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
What Are Common Non-Surgical Treatment Options Available?
Common non-surgical treatment options include conservative pain management techniques such as physical therapy, medication, and spinal injections, alongside alternative treatment modalities like acupuncture and chiropractic care, all supported by evidence-based practice to alleviate back pain effectively.
How Often Should I Follow up With a Specialist?
The follow up frequency for back pain specialists is contingent on individual patient needs, clinical progress, and treatment plans. Appointment scheduling typically aligns with evidence-based guidelines, often recommending bi-weekly or monthly evaluations to optimize therapeutic outcomes.